ESSENTIAL QUANTUM PHYSICS
PETER LANDSHOFF
University of Cambridge
ALLEN METHERELL
University of Central Florida
GARETH REES
University of Cambridge
(Cambridge University Press)
This book provides a first course on quantum mechanics and describes simple
applications to physical phenomena that are of immediate and everyday
interest.
The first five chapters introduce the fundamentals of quantum mechanics and
are followed by a revision quiz with which readers may test their
understanding. The remaining chapters describe applications, including the
theory of spin and its application to magnetic resonance imaging, physics
of lasers, molecular binding, simple properties of crystalline solids
arising from their band structure, and the operation of junction
transistors.
Ideal either as a course text or a self-study text, the book contains
nearly 100 exercises and hints to their solution.
Contents
1 Preliminaries
Atoms; Photons; Wave nature of matter; Problems
2 The Schroedinger equation
Wave functions and operators; Example: the one-dimensional
potential well; Probability interpretation and normalisation; Beams
of particles; Continuity conditions; Problems
3 Special solutions
Particle in a box; The one-dimensional square well; The linear
harmonic oscillator; The tunnel effect; The delta-function
potential; The WKB approximation; Alpha decay; Problems
4 The superposition principle
Linear operators; Wave packets; Ehrenfest's theorem; Hermitian
operators; Operators and observables; Commutators; Problems
5 The hydrogen atom
Good quantum numbers; Orbital angular momentum; Spherically
symmetric potentials; The hydrogen atom; Many-electron atoms;
Two-body systems; The deuteron; Problems
Revision quiz
6 The hydrogen molecule
The ionised hydrogen molecule; Other molecules; Problems.
7 Introduction to perturbation theory
Time-independent perturbation theory; Time-dependent perturbation
theory; Transition probability; Energy uncertainty principle;
Sudden change in the Hamiltonian;
Example: decay of tritium; Problems
8 Spin
Two kinds of angular momentum; Spin half;
The electromagnetic interaction; The Zeeman effect;
Spin precession; Problems
9 Masers and lasers
Radiative transitions; Resonant absorption and stimulated emission;
Electric dipole transitions; The ammonia molecule; The ammonia maser;
Population inversion; The laser; Holography; Problems
10 Band structure of crystals
Electrons in crystals; Band structure; Number of levels in a band;
Band overlap; Simple consequences of band structure; Problems
11 Electron motion in crystals
Electron velocity; Motion in an external electric field; Electric
current; Effective mass and holes; Thermal excitation; Pair
excitation in intrinsic semiconductors; Problems
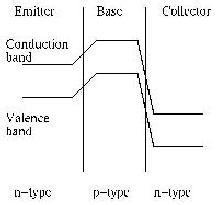
12 Transistors
Impurities; n- and p-type semiconductors; Impurities and crystal
colour; Semiconductor junction; The diode; The junction transistor;
Two simple circuits; Problems
Appendices
A Power-series solutions
B The delta function and Fourier transforms
C Orbital-angular-momentum operators
D Electrodynamics
E Bloch waves
Hints for the problems
Click here for the first chapter of the book.

